Research interests
My research interests broadly span robot learning, with a focus on vision language action models and diffusion-based approaches for tasks involving mobile manipulation, long horizon planning, dexterous manipulation or super human performance. Specifically, I am curious about hierarchical approaches and approaches that support continual learning.
-
Mobile manipulation
-

Dexterous manipulation
-
Continual Learning
Projects
-
Continuous-Time Diffusion Policies for Visuomotor Control:
A Stochastic Calculus PerspectiveWe reframed diffusion policies as controlled SDEs (Variance Preserving / Variance Exploding / Critically Damped Langevin Dynamics) for visuomotor control. Then, we implemented multiple samplers and compared robustness on the PushT benchmark. Our experiments found that VP-SDE performs best and most consistently (≈0.78-0.80 success).
-

GeoVision: Fine-Grained Urban Geolocation in San Francisco via Distribution-Aware Visual Models
GeoVision predicts where a street photo was taken within San Francisco using a Vision Transformer (StreetCLIP) plus custom geolocation heads. A 31x31 grid classifier reaches 66.8% top-1 accuracy, while a probabilistic Gaussian head achieves ~600m mean localization error and provides uncertainty estimates. The project includes map-based visualizations and attention rollouts to show what cues the model uses when localizing images.
-

MARIO: Reinforcement Learning on Image Observations
We trained PPO and DQN agents to play Super Mario Bros directly from raw pixels (stacked grayscale frames with the full 12-action control space). Our best agent achieved a completion rate of 96.32% on Level 1-1 using PPO and a top-k pseudo-greedy inference strategy. This performance is compared against other PPO and DQN agents. We investigated how architecture and preprocessing influences performance and evaluated transfer performance from Level 1-1 to Level 1-2.
-
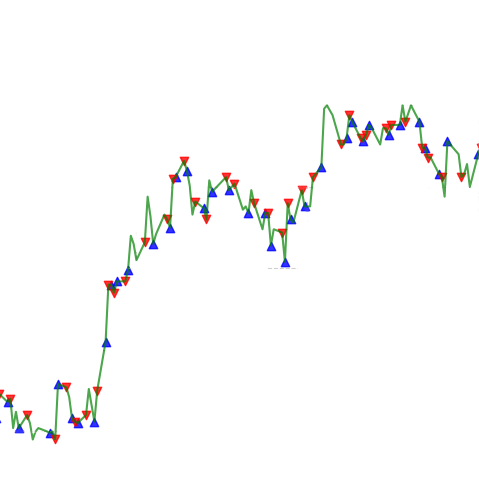
A Comparative Study of Trading Using Deep Q-Learning and Double Deep Q-Learning in Niche Markets
We investigated whether reinforcement-learning trading agents can perform well in niche markets by modeling trading as an MDP and comparing DQN vs Double DQN across three different action-space designs. Using data of the First North Growth Market and Novotek (with OMX30 as context), we evaluated performance with ROI and Sortino ratio across multiple runs for two assets. We showed how action-space choice influences stability and trading behavior, and that Double DQN generally delivers more robust risk-adjusted performance than standard DQN.
-

Predicting Hospital Readmission from Clinical Discharge Summaries
We built a machine-learning pipeline to predict hospital readmission risk using only free-text discharge summaries from the MIMIC-IV dataset. We compared multiple text representations like keyword features, ClinicalBERT embeddings, and LLM-generated summary embeddings across several classifiers (Logistic Regression, tree models, XGBoost, and a neural net). Our best model (a Random Forest on LLM-based embeddings) achieved roughly F1 ≈ 0.79 and Accuracy ≈ 0.74, showing that clinical notes contain a signal for readmission prediction.